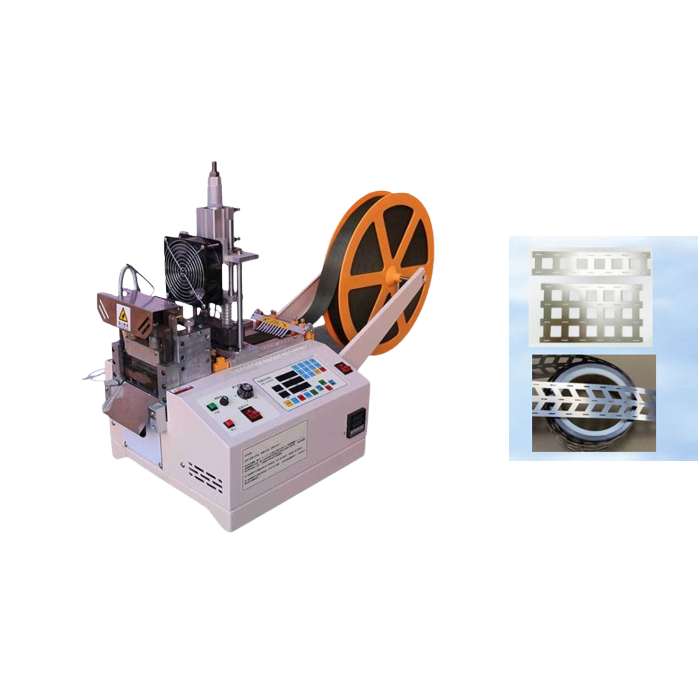
What types of Velcro materials can be cut with a machine?

A variety of Velcro materials used in industrial applications, all compatible with automated cutting machines.
Cutting different types of Velcro by hand often leads to fraying, length inconsistency, and production delays.
Most Velcro cutting machines1 are compatible with a wide range of hook-and-loop tapes, including nylon, polyester, adhesive-backed, flame-retardant, and elastic Velcro.
Velcro cutting machines are versatile tools designed to efficiently process a wide range of materials, including standard hook and loop (Velcro) tape, woven tape, shoelaces, safety belts, and other soft goods. They also handle electronic materials like heat-shrink tubing and insulation tape. Certain models are specialized for tougher materials such as webbing, ribbons, and leather, making them ideal for both textile and industrial applications. This adaptability enhances productivity across various manufacturing sectors.
If you’re wondering whether your specific Velcro material can be cut by machine, here’s a breakdown that will help you avoid mismatches and maximize cutting efficiency.
Which kinds of Velcro tapes are compatible with different machines?

A reference chart displaying various Velcro tape types and their recommended cutting machines for optimal performance.
Velcro isn’t just Velcro. Materials vary by composition, flexibility, coating, and thickness—and not every machine can handle all types.
Compatibility depends on the tape’s material, backing, and thickness. Suzhou Haoxinhe’s machines are adaptable to most standard industrial Velcro types.
Understanding how each type of Velcro interacts with cutting mechanisms will help you choose the right machine and avoid production issues.
🧵 Common Velcro Tape Types
Let’s start with a list of Velcro materials and their typical characteristics:
| Velcro Type | Material | Common Use Cases | Machine Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon Hook-and-Loop2 | Nylon | Garments, medical wraps, cable organizers | Hot and cold cutting machine |
| Polyester Hook-and-Loop | Polyester | Outdoor gear, marine products | Webbing ribbon cutting machine |
| Adhesive-Backed Velcro3 | Nylon/Polyester + Glue | Industrial assembly, signage | Bubble wrap cutting machine with low-temp blade |
| Elastic Velcro | Blended fabric | Wearables, sports gear | High-speed trademark cutting machine with tension control |
| Flame-Retardant Velcro | Coated Nylon | Automotive, aerospace | Protective foam cutting machine with sealed edges |
| Back-to-Back Velcro | Dual-loop | Cable bundling, office use | Rotary bevel cutting machine |
🏭 Machine Compatibility Explained
Here’s how different cutting technologies align with various Velcro types:
1. Hot and Cold Cutting Machine
- Best for: Nylon and polyester tapes
- Why: Hot blades seal the edges and prevent fraying, while cold blades preserve fabric properties in heat-sensitive materials.
- Used by: Garment factories, medical equipment producers
2. Webbing Ribbon Cutting Machine
- Best for: Thick or coated polyester Velcro
- Why: Reinforced feeding system handles high-tension tapes; clean, angled cuts possible with optional rotary blades.
- Common in: Outdoor gear production, tactical industries
3. Bubble Wrap Cutting Machine
- Best for: Adhesive-backed Velcro
- Why: Precision temperature control keeps glue from melting; low-speed cutting reduces residue build-up.
- Ideal for: Electronics and promotional item packaging
4. High-Speed Trademark Cutting Machine
- Best for: Thin elastic Velcro
- Why: Speed and flexibility in tension adjustment make it ideal for soft, stretchable materials.
- Used by: Sportswear, rehab gear manufacturers
5. Protective Foam Cutting Machine
- Best for: Flame-retardant Velcro
- Why: Fully enclosed blades and temperature controls minimize flammable risk.
- Standard for: Automotive interiors, aerospace gear
6. Rotary Bevel Cutting Machine
- Best for: Dual-loop back-to-back Velcro
- Why: Custom angles and controlled feeding help prevent overlap or curl.
- Great for: Cable management solutions, utility kits
💡 Tips to Choose the Right Cutting Solution
When selecting a machine from Suzhou Haoxinhe Electrical Equipment Co., Ltd., I always recommend clients to:
- Send material samples first for test cuts.
- Confirm thickness and width range compatibility.
- Specify coating types like adhesives or flame retardants.
- Discuss volume and speed expectations upfront.
These steps reduce return rates and ensure that the cutting line runs smoothly from day one. Our custom-cutting solutions are designed to handle variation and scale.
Conclusion
Different Velcro types require different cutting technologies—know your material before choosing the right machine.
Insights
In my 20 years working with cutting automation systems, the most common mistake I’ve seen clients make is relying solely on machine specs when choosing equipment for Velcro cutting. What really matters isn’t just what the machine says it can cut, but how it handles your specific batch of Velcro under real-world factory conditions.
Even within “nylon Velcro,” for instance, I’ve seen variations in weave density and chemical coatings that drastically affect cut quality and edge sealing. This is why top-tier manufacturers always run material compatibility tests—preferably on-site or via pre-shipment samples—before finalizing machine orders.
Machines like Suzhou Haoxinhe’s are robust and adaptable, but matching them correctly requires knowing not just the material type but the intended application (medical, aerospace, etc.), as tolerances and compliance needs vary. For any manufacturer serious about scale or precision, a test-first policy is the real game-changer in machine selection.
Explore this link to discover top-rated Velcro cutting machines that enhance efficiency and precision in industrial applications. ↩
Learn about the diverse applications of Nylon Hook-and-Loop in manufacturing, from garments to medical wraps, and how it can benefit your projects. ↩
Find out how Adhesive-Backed Velcro is utilized in industrial assembly, enhancing efficiency and versatility in various applications. ↩